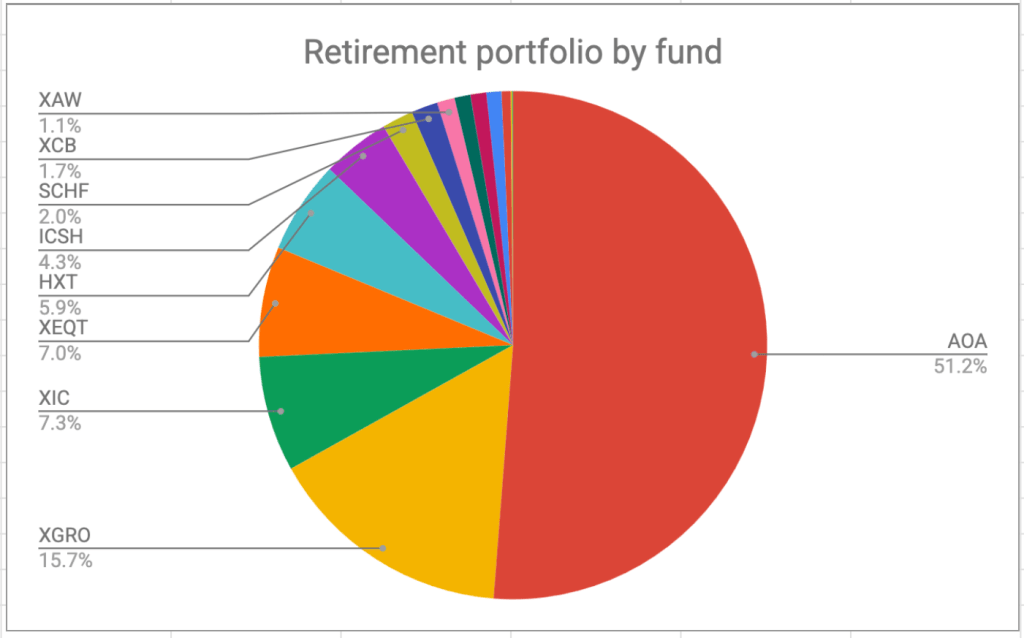
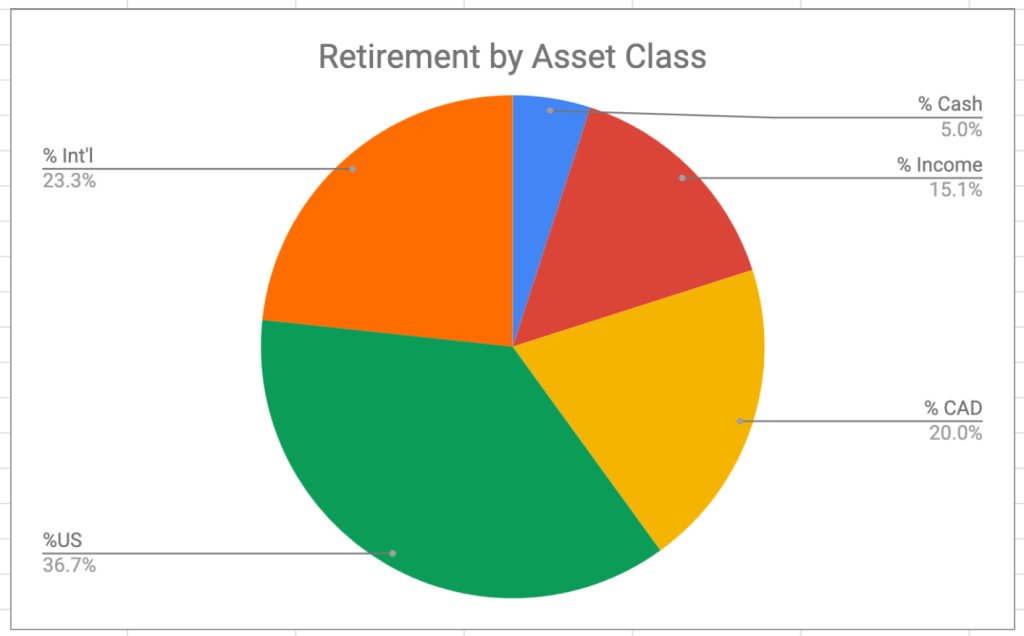
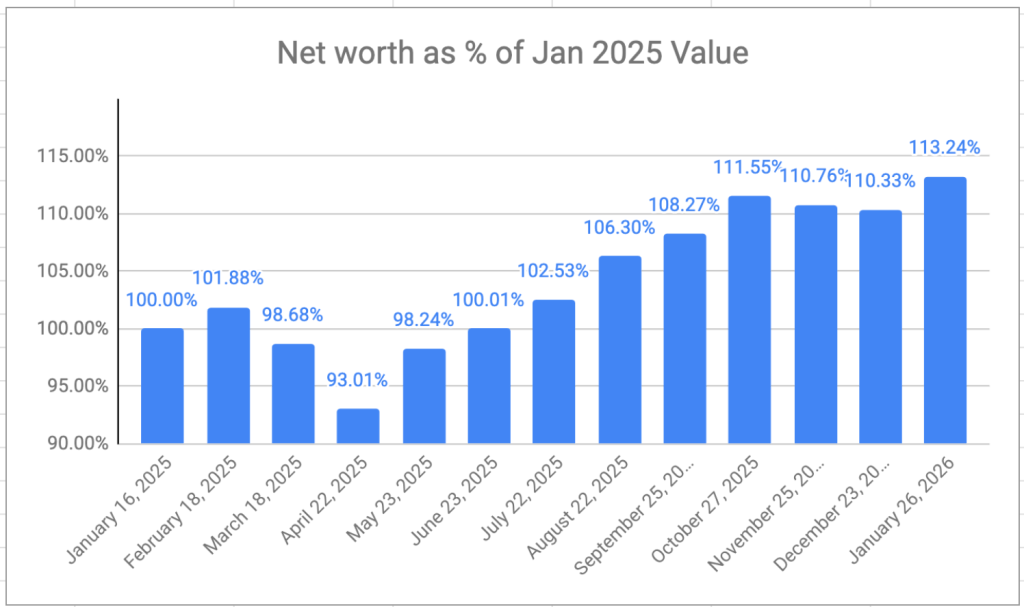
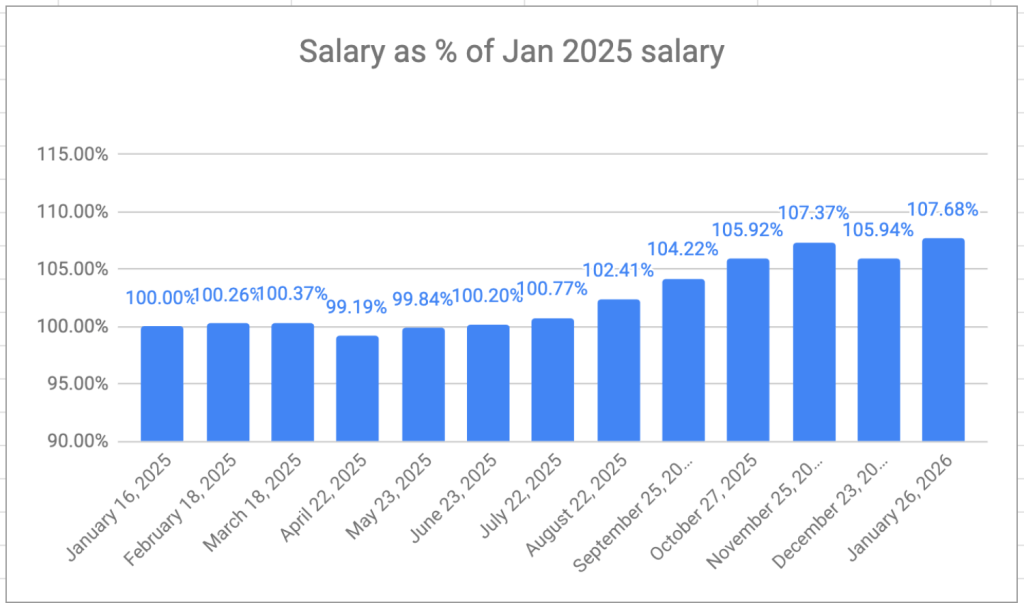
One of the confusing questions I got from my international colleagues when I announced my retirement was “what’s the retirement age in Canada”? And, after thinking about it, said, “There isn’t one that I know of”, which is, strictly speaking, correct.
However, for many Canadians (and, I suppose, for many people around the world), “retirement age” equates to “the age where I can collect my pension”. For me, the equivalent statement was “the time when my retirement savings were sufficient1” (you can read about the steps I took here). I don’t have a private pension through my employer, so CPP, OAS and my own savings are all I have to sustain my needs throughout retirement.
CPP (Canadian Pension Plan) and (possibly2) OAS (Old Age Supplement) are two sources of income that will eventually make up part of my retirement income, but not for a while. For the time being, my retirement income comes from a mix of non-registered asset sales (about 2/3 of my 2025 household income) and RRIF payments (about 1/3 of my 2025 household income)3. My advisor suggested waiting as long as possible to collect on CPP/OAS, which is age 70 for both.
But maybe, if you haven’t retired yet, you haven’t really thought too much about these things4? Here’s a quick primer.
What’s CPP and what’s it worth to me?
CPP applies to anybody who has contributed to the plan; how much you contribute annually is captured on your T4 slips. You can see your lifetime contributions5 by logging into your My Service Canada Account. It is the history of these contributions6 that ultimately determine what your annual pension will be in the year you first start taking it.
The first year you are eligible to receive CPP is the year you turn 607; every month you wait after turning 60 increases your monthly payment. The absolute maximum CPP you could collect would be waiting until you turn 708. The Feds lay it all out here.
The absolute maximum monthly CPP you could possibly get as a 65 year old is $1507.65 in January 2026 per the Feds9. Since I retired early, and 18 year-old me worked a part-time minimum wage job, my CPP will be less than that. (The CPP calculation takes your best 32 years of earnings into account).
What’s OAS and what is it worth to me?
OAS (“Old Age Security”) applies to anybody who has lived in the country long enough10. OAS can start at age 65, and be delayed until as late as age 70. Like CPP, OAS rewards those who start payments later than age 6511. You get an OAS supplement of 10% when you hit 75.
The absolute maximum monthly OAS payment in the first quarter of 2026 is $742.31 if you’re under 75 and $816.5412 if you’re over per the Feds. (These amounts are adjusted every quarter in accordance with inflation rates.)
The wrinkle with OAS is that it’s income-tested. If you make too much money, you’re going to have to pay some of it back. If you really make too much money, you’ll have to give it all back. This is commonly known as “OAS Clawback”13.
The magic of CPP and OAS
CPP and OAS payments are both indexed to inflation, for as long as you collect it. This is key for me personally — none of my other income sources are inflation-proof, so the more I can get that is inflation-protected, the better. That’s part of the reason I’m planning on delaying collecting CPP and OAS until I’m 70 — that way, I can maximize the inflation-protected income. The other reason I’m delaying these payments is to try to avoid OAS clawback. The earlier I take RRIF money out, the lower my RRIF income will be later in retirement, when I have to start adding CPP to my income. I have no idea if I will avoid the clawback because it depends on the performance of specific elements of my portfolio. But try I will.
Estimating CPP and OAS for VPW
My decumulation strategy is based on VPW (Variable Percentage Withdrawal). I’ve talked about it previously over here and here. VPW requires, as an input, the value of a future pension. So how do I go about estimating that? Any reasonable estimate might want to ignore what the feds put on the periodic CPP summaries they send out because those estimates are assuming you’re retiring at 65, and working at a similar salary level (of course, if that’s your plan, then it’s perfectly fine — but it wasn’t mine :-))
All good estimates start from the lifetime contributions table you can find at My Service Canada. From there I’ve given a few tools a spin:
PWL Capital Tool
https://research-tools.pwlcapital.com/research/cpp
This tool has a lot of neat features, but be careful. The model bakes in both inflation estimates and wage inflation estimates that are changeable, but not immediately obvious.
CPP Calculator
https://www.cppcalculator.com/
This is one I recommended previously in Tools I Use, but the upload feature has been broken for a while now. It still works by entering it manually, but I now prefer the tool below….
Finiki CPP and QPP Calculator
https://www.finiki.org/wiki/CPP_and_QPP_calculator
The Finiki tool is now my favourite because it’s available as a worksheet (Google Sheets, Excel and Libre Office all supported), and all you need to do is enter in your pension contributions. The current version (2.3) hasn’t been updated with the latest YMPE values, but it’s a trivial exercise to update them.