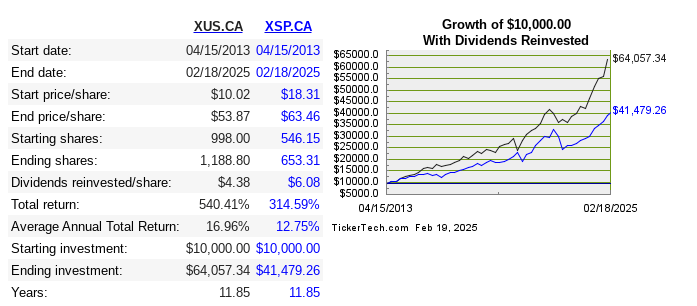
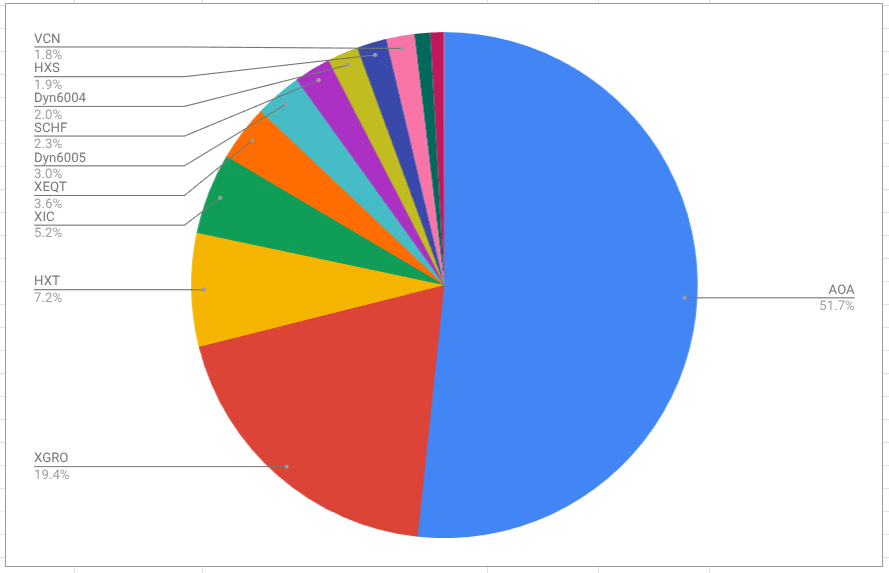
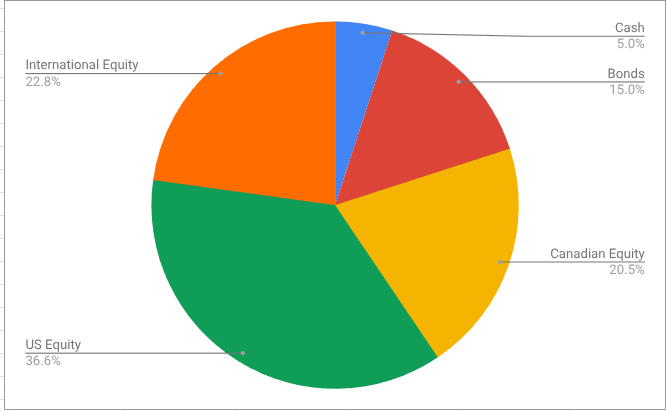
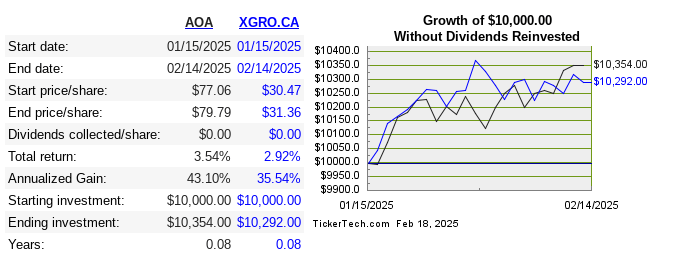
I’m not sure when I first made a purchase of a USD-denominated ETF. Probably over 10 years ago. Clearly, I thought it was a good idea, because as of today I find that 57% of my retirement savings1 are denominated in US Dollars.
And unlike other people I’ve talked to, there’s no underlying rationale for that. I’ve never earned employment income in USD and I don’t own property in the US. So why?
I’m a cheapskate.
I started investing in USD based ETFs simply because they were a much better deal than their Canadian equivalents. This is less true now than it used to be, but it’s still true. Take for example the comparison between comparable USD and CAD ETFs that track the same index:
| Index | What’s in it | USD ETF | MER | CAD ETF | MER |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S&P 500 | Top 500 US stocks | IVV | 0.03% | VFV, XUS | 0.09% |
| Russell 2000 | 2000 mid-market US Stocks | VTWO | 0.07% | XSU2, RSSX3 | 0.36% for XSU, 0.25% for RSSX |
| FTSE Developed ex US | Global stocks outside of the USA | SCHF | 0.06% | VDU | 0.22% |
The Canadian market has become more competitive, and MERs have come down, but given the size of the US market, it’s still cheaper to invest there.
I’m not a very savvy cheapskate.
So although the MERs of US ETFs were stunningly attractive, I failed to consider the cost of currency conversion. For this I blame naivete as well as a lack of transparency on the part of my provider. It was not possible for me to easily figure out how much each CAD to USD transaction was costing me. A good estimate is about 1.5% the cost of the transaction, but some providers make this much cheaper5.
I also had USD investments in my TFSAs, which, from a tax perspective, isn’t the best idea.
Over time, I discovered the joys of Norbert’s Gambit to do currency transactions on the cheap and I became more savvy. And I eliminated all US holdings from my TFSA.
Preparing for Retirement
In preparing my portfolio for retirement (steps I took are outlined here), I did seriously consider converting everything to CAD in the interest of keeping things simple. I did not, and here’s why:
- I figured that having ready access to USD would be rather useful to retired me, since I do vacation there. And I had made other preparations in light of that, setting up a USD credit card and USD savings account for RRIF payments to go to.
- Although I knew that having USD RRIFs would make getting paid in retirement more complicated, I thought I had worked out a plan with my provider6 that would make extracting USD RRIF payments achievable, with some effort on my part.
- I sort-of liked having some of my investments in USD since it’s a stable currency. Usually.
- I also liked the additional boost I got from USD HISAs. (That’s probably an anomaly but one I’m happy to take advantage of)
- I could change my mind at any time.
Current Reality
This isn’t working like I thought it would.
My provider decided to backtrack on allowing me to extract USD from my USD RRIF;7 we’re still going back and forth on that front, but my friends at QTrade are on my naughty list as a result. I’m not hopeful.
What it means practically is that although the value of my USD RRIF is used to calculate my RRIF minimums, I can only withdraw RRIF payments from the Canadian side. At present, the Canadian side of my RRIF will fund my RRIF minimum payments for a while, but at some point I’ll have to use Norbert’s Gambit to move funds from the USD RRIF to the CAD RRIF.
My Advice
I don’t think that holding USD assets in retirement — especially in a RRIF — is a great idea for the DIYer. Unless platform providers give really clear processes8 for how to extract that money from a USD RRIF, expect trouble.
At some point, I will either switch providers to find one that supports my requirements9, or I will convert everything to CAD. Right now, I have a process that works, but older me I expect will find it too complicated.
- Majority of the USD holdings are in my / my spouse’s RRIF; small portion is in my non-registered account. ↩︎
- Not an apples to apples comparison, admittedly. This ETF is hedged so it’s less impacted by changes in the CAD/USD exchange rate but this comes at a cost. ↩︎
- This is ALMOST the same thing; RSSX uses a capped version of the index ↩︎
- And try as I might, I couldn’t find a USD ETF that invested in the TSX/S&P 60. Not really surprising, and my USD retirement holdings have very limited Canadian exposure. AOA has about 2.4% Canadian exposure. ↩︎
- Notably, Interactive Brokers and lately, Wealthsimple especially if you hold more than 100k with them. ↩︎
- Involving multiple phone conversations and multiple emails ↩︎
- You may ask, “what’s the point of having a USD RRIF if you can’t extract USD from it”? I had the same question… ↩︎
- RBC says they support it and so does Questrade. ↩︎
- I had sorely hoped Wealthsimple could be that provider, but (sigh) they don’t support spousal RRIFs at the moment. ↩︎