As summer shifts into fall, I’m reminded that it’s back-to-school time. Or “Dad, I need money for tuition” time. I still have kids attending higher education, still making withdrawals from the family RESP we set up shortly after the birth of son #1, almost 25 years (!) ago now. RESP investing is a bit different from retirement investing given the (hopefully) shorter timelines of RESP investing1. Here’s how I approach it.
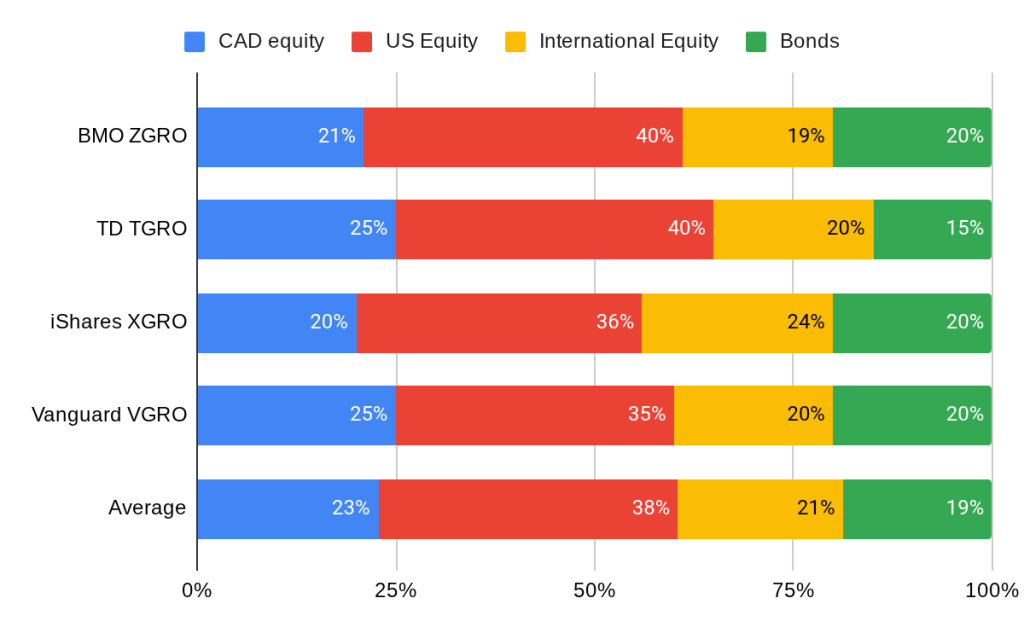
In the early days of the RESP, the contributions were invested in mutual funds; these were dark days, long before the rise of very cheap ETFs. Mutual funds were the ONLY way to make routine contributions (which I made, monthly, without fail — Pay Yourself First and all that). I had an 80/20 mix of equities and bonds in the first 18 years or so of its existence: 4 funds, one for US Equity, one for Canadian equity, one for international equity and one for bonds. I don’t remember the specifics of which ones and what percentages exactly. But the fund kept growing, thanks to market returns as well as CESG grant money, which I took full advantage of2!
As son #1 came close to entering post-secondary studies, I shifted the portfolio to a 60/40 mix using individual ETFs like HXS for US Equities, HXT for Canadian Equities, HXDM for International Equities, and CBO for Bonds. The GlobalX funds didn’t throw off dividends3 and so I just had to deal with the periodic (monthly) distributions of CBO, which ultimately were set to DRIP4.
I made the decision to move to 60/40 over 80/20 to preserve a bit more of the capital in the event of some kind of market meltdown5. Growth gets curtailed somewhat as a result, but there’s less volatility.
But I finally realized that all of this was completely unnecessary thanks to all-in-one ETFs. So now, the RESP has exactly ONE holding — XBAL, an all-in-one from iShares that takes care of the 60/40 split for me. And this is set to DRIP as well, so every quarter the RESP picks up a few more XBAL shares.
You can see how XBAL has preformed over the past 15 years or so. I’m comparing it to the 80/20 XGRO ETF from the same family, one that features prominently in my ETF All-Stars page6:
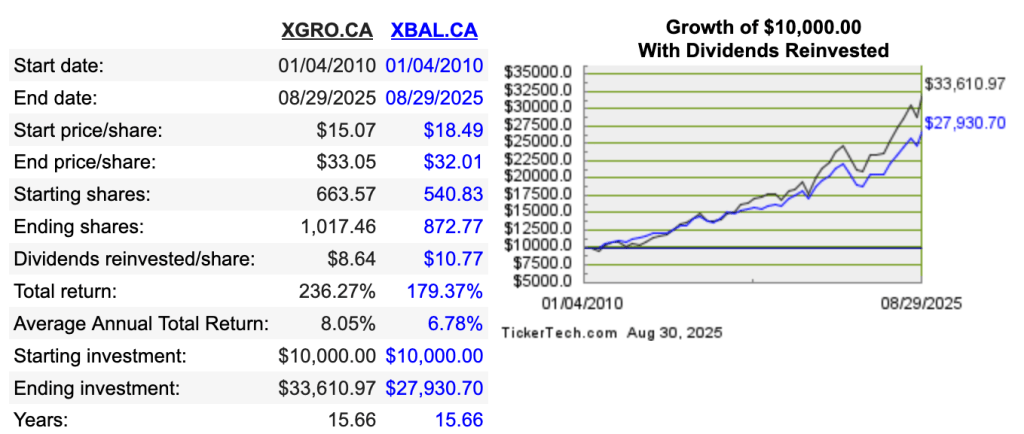
In a future post, I’ll explain how I fairly divide the RESP among my two sons — in essence, I pretended that the RESP was a mutual fund, with each son receiving the same number of units on the day the first withdrawal was made. Withdrawals are henceforth made in units, not dollars, and the unit price fluctuates with the value of the RESP.
How are you managing your RESP? Let me know at comments@moneyengineer.ca.
- Less time to build wealth, shorter runway for decumulation ↩︎
- As a certified cheapskate, it’s hard for me to resist free money of any kind. ↩︎
- They are “corporate class” ETFs that use a clever structure to avoid paying out dividends; all growth is buried in the increase of the ETF’s price. I still hold some of these in my non-registered accounts. ↩︎
- Dividend Reinvestment Plan. Instead of getting cash in the RESP account, the DRIP buys additional shares of whatever generated the dividend in the first place. ↩︎
- One may ask why I chose to stick with 80/20 in retirement, which is against some conventional wisdom. I figured that the RESP decumulation phase would be over a much shorter time period (say 5-10 years) and so I would be less able to wait for a market bounce-back. In retirement, I’m hopeful that decumulation will take much, much longer, and so with 80/20 I have a better chance of outliving my savings. ↩︎
- Chart is courtesy http://www.dividendchannel.com, featured on Tools I Use. When I rolled the comparison all the way back to 2007 the 60/40 XBAL actually OUTPERFORMED the (supposedly) more risky XGRO. Can’t explain that one. ↩︎