This is a (hopefully monthly) look at what’s in my retirement portfolio. The original post is here. Last month’s is here.
Portfolio Construction
The retirement portfolio is spread across a bunch of accounts1:
- 7 RRIF accounts (3 for me, 3 for my spouse, 1 at an alternative provider as a test)
- 2 TFSA accounts
- 5 non-registered accounts, (2 for me 1 for my spouse, 2 joint)
The target for the overall portfolio is unchanged:
- 80% equity, spread across Canadian, US and global markets for maximum diversification
- 15% Bond funds, from a variety of Canadian, US and global markets
- 5% cash, held in savings-like ETFs.
The view as of this morning
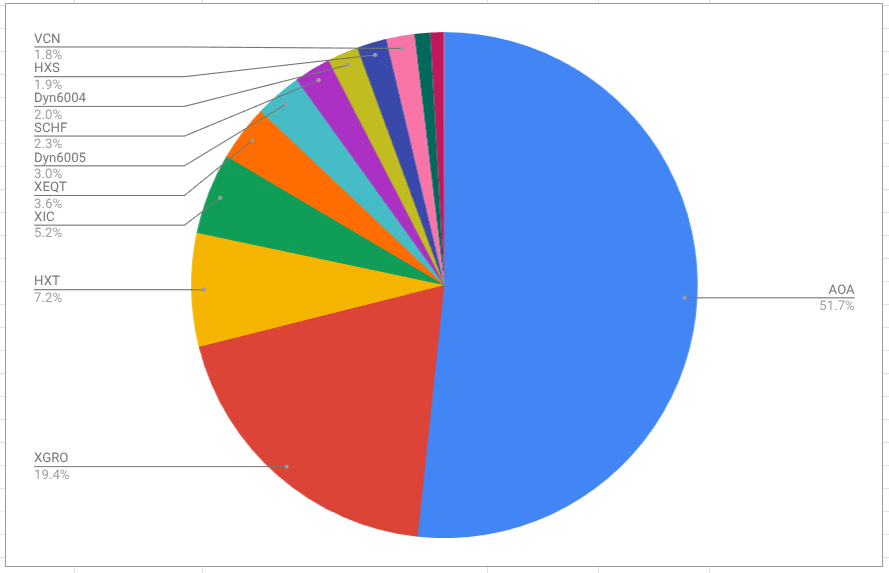
As of this morning, this is what the overall portfolio looks like:

The portfolio, as always, is dominated by AOA and XGRO which are 80/20 asset allocation funds in USD and CAD, respectively. The rest are primarily either cash-like holdings in two ETFs: ZMMK2 in CAD and ICSH3 in USD) or residual ETFs held in non-registered accounts for which I don’t want to create unnecessary capital gains just for the sake of holding AOA or XGRO.
The biggest month over month change is due to switching brokers. My old broker (QTrade) allowed the purchase of HISAs, but my new broker (Questrade) doesn’t seem to offer them4. So I replaced DYN6004 with ZMMK and DYN6005 with ICSH. I made these changes in my QTrade account to avoid any problems with doing an “in-kind” transfer to Questrade.
I’m still in need of USD to pay off some vacation bills, so there is a small hit to SCHF to help out.
Plan for the next month
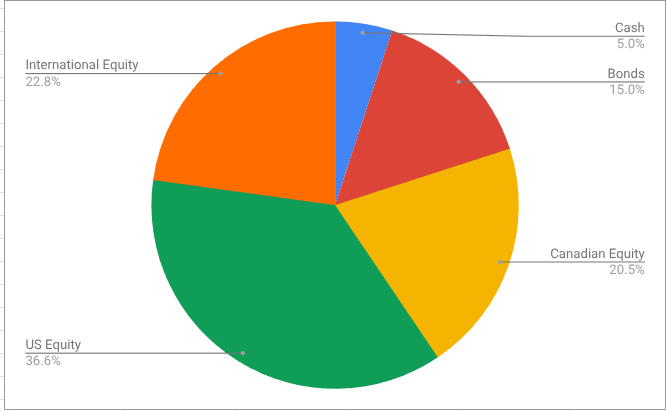
The asset-class split looks like this
The international equity percentage is below my target of 24%, and so I’ll have to fix that5. VEU looks like it provides exposure to both developed and emerging markets at a rock-bottom price6. XEF would be a perfect fit in the Canadian market, although I should probably also consider XEC to get some emerging markets exposure.The cash position is artificially high because I already did the necessary transactions to get paid out of my RRIF and non-registered accounts (if I did this exercise at the beginning of the month, rather than mid-month, that would disappear). That extra cash will flow to my bank account in the coming days.
A quarterly activity that I’ll be performing this month7 is to shift some of my USD RRIF holdings into my CAD RRIF. I do this to make sure I’m not overexposed to changes in the CAD/USD exchange rate. My current provider reportedly allows me to make RRIF payments natively in USD, so that may be another option to consider. I’ll make an attempt at some point!
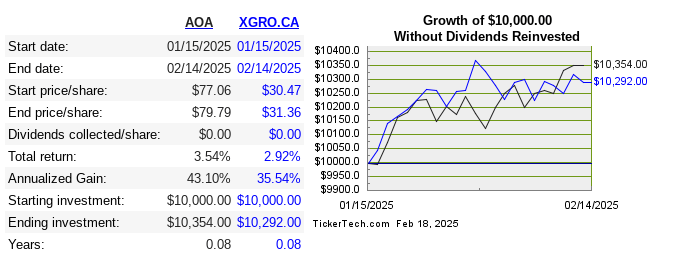
One final note: my retirement savings declined 3%8 over the month due to the wild (mostly downward) swings in the stock market, but this leaves me roughly even since my retirement started at the beginning of the year. Here’s the monthly returns for the 2 ETFs that make up the lion’s share of my portfolio9.
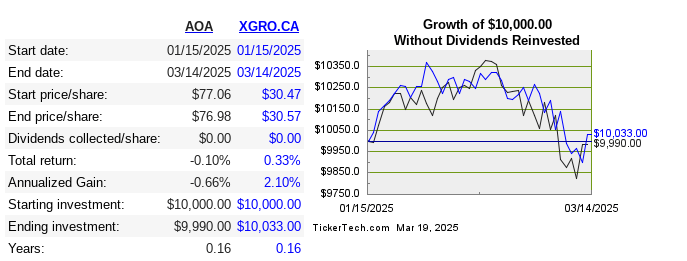
- The list is sort-of accurate. I’m in the middle of changing online brokers and since Questrade combines USD and CAD assets in one account, the number of accounts is diminishing. ↩︎
- Current 12-month yield: 3.6% ↩︎
- Current 30-day SEC yield: 4.61% ↩︎
- This specific topic addressed at https://www.financialwisdomforum.org/forum/viewtopic.php?t=125308. ↩︎
- The observant reader will note I also said this LAST month. That was before I decided to switch brokers. Once my holdings settle at Questrade, I’ll revisit. ↩︎
- MER = 0.04%. VEU has some Canadian exposure too, which isn’t ideal, but I don’t think there’s a USD ETF that excludes both Canada and the USA. ↩︎
- And should have done last month, sorry. ↩︎
- It would have been worse, except the USD also went up versus the Canadian dollar in the time period. Diversification works 🙂 ↩︎
- “Without dividends reinvested” since these two ETFs only pay out quarterly. There haven’t been any yet — next month! ↩︎