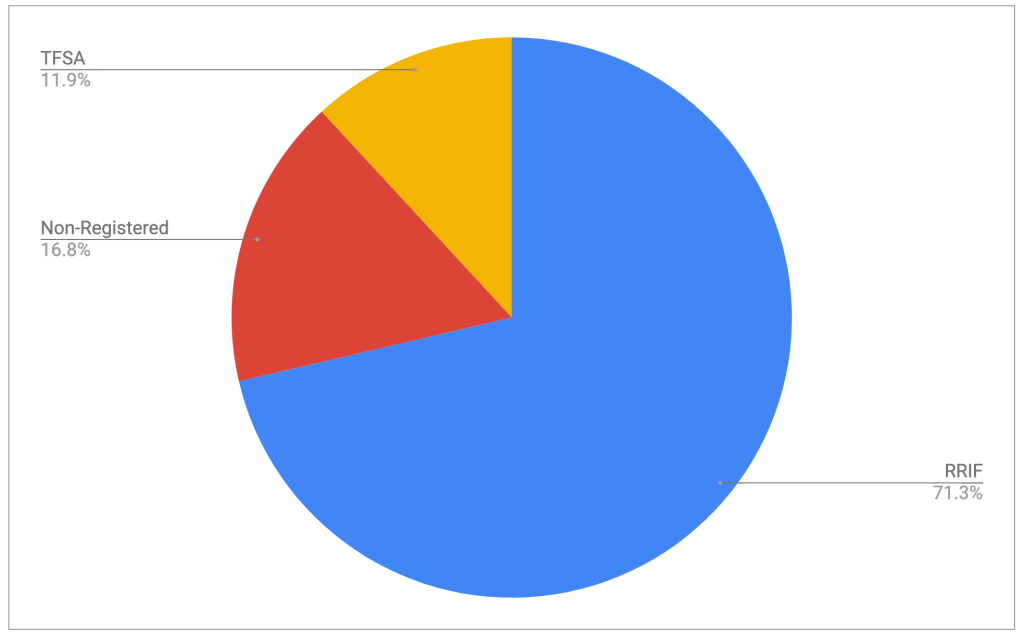
My retirement portfolio is spread across multiple brokers and multiple accounts. And although I treat the portfolio as a unified entity when it comes to asset allocation (the concept is discussed here), different accounts have different allocations. The reasons are varied, but I would rank inertia as one of the big contributors — sticking with what’s there seems like a lot less effort than the other options.
What I think in important to point out is that the portfolio is still dealing with inflows and outflows every single month:
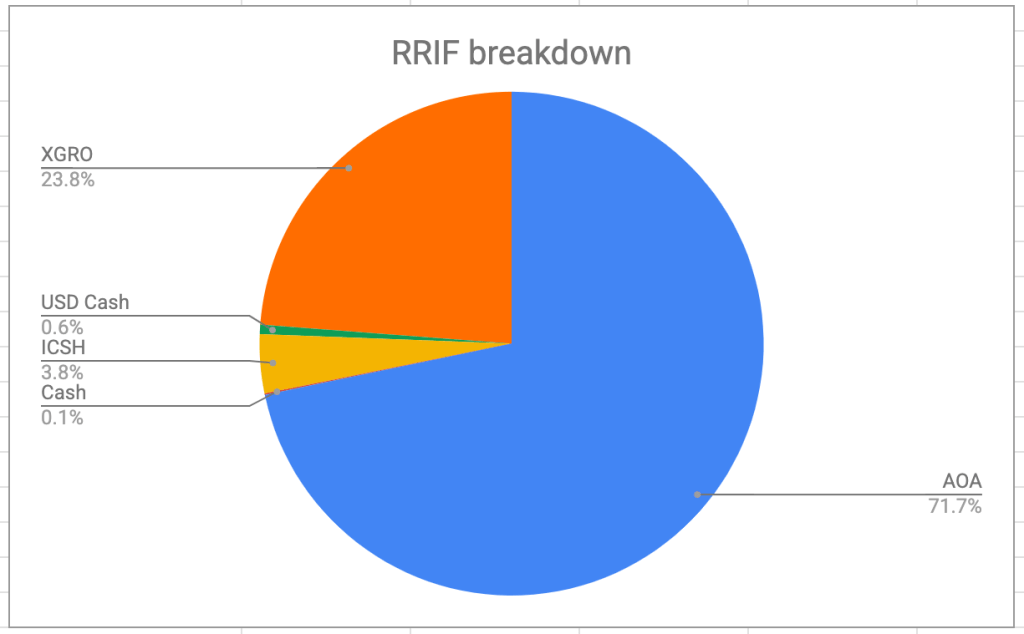
- I pay myself RRIF minimum from my RRIF accounts, and this usually means selling some shares of XGRO
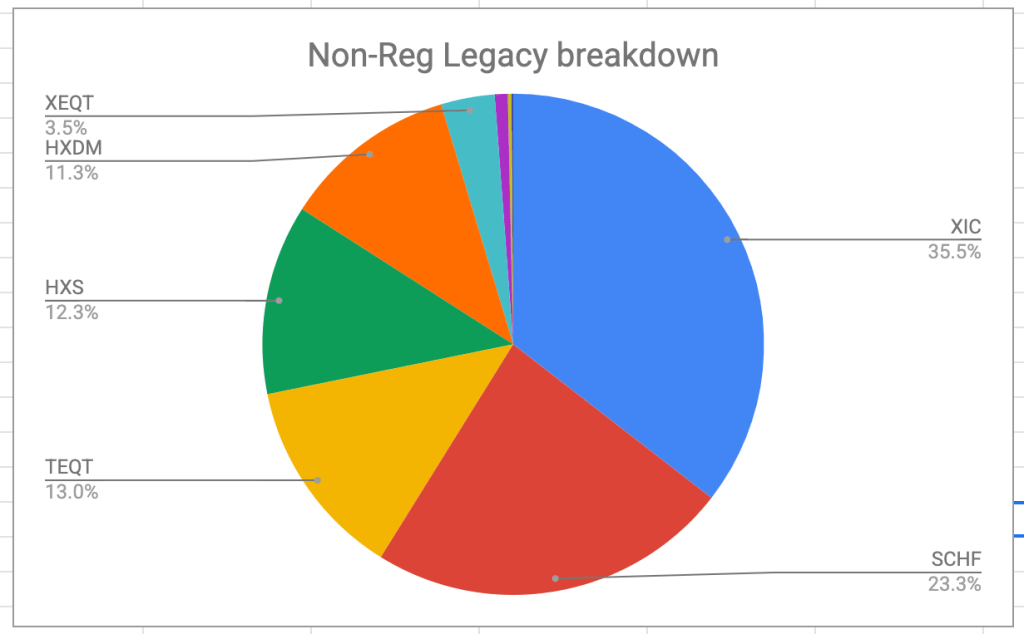
- If RRIF minimum isn’t sufficient for my expenses (and it hasn’t been), then I have to liquidate shares from my non-registered account.
- I contribute to our TFSAs every month
- Questrade gives me free money every month as a reward for shifting assets their way (see how I did it here). This money shows up in my non-registered accounts1.
- Dividends show up every month2; every quarter there is an even bigger distribution
- And quarterly I convert some of my AOA holdings to XGRO within my RRIF using Norbert’s Gambit3. When I do this, it reduces my US and international equity holdings and replaces it with Canadian equity4.
So given all these ins and outs, there are always opportunities to tweak the asset allocations so that they remain close to my targets.
The targets, as always, are unchanged:
- 5% Cash (mostly ultra short-term bonds)
- 15% bonds
- 20% Canadian Equity
- 36% US Equity
- 24% International Equity
Last week, a reader’s question (please send questions or comments to comments@moneyengineer.ca) led me to take a different look at what was in each of my retirement accounts (RRIFs, TFSAs, non-registered), and this week I acted on correcting a flaw in the way the accounts were structured.
The reader was actually asking about foreign withholding tax implications since the rules are different depending on whether the asset is held in non-registered, TFSA or RRIF but after spending a lot of time looking at it, I decided that, from a tax perspective, the portfolio was actually in reasonable shape. (If you want to dive into this yourself5, you can read https://www.finiki.org/wiki/Foreign_withholding_taxes and https://pwlcapital.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/2017-12_Ben-Felix_WP_Asset-Location-Uncertainty.pdf).
But this study did make me realize that the small allocation I had of bonds in my TFSA was wrong-headed. Since in my planning the TFSA is the LAST place I’ll head to fund my retirement, it follows that it should have the longest-timeline investments. So, for me, that means 100% equity is the correct allocation for the TFSA accounts. So what did I do?
- I sold the bonds in my TFSA (XSH was the ETF), and put them in my RRIF (choosing instead to use XCB, a longer-duration corporate bond fund)
- Of course, since you can’t add money to a RRIF, something had to be sold there. XGRO was plentiful, so that’s how I funded the bond purchase. From an asset allocation perspective, selling XGRO meant that I reduced my Canadian, International and US Equity exposure at the same time.
- To compensate, the cash I generated in my TFSA by selling XSH was used to buy a combination of XIC (Canadian Equity) and XAW (US and International equity combined). XIC was already in the TFSA6. XAW is new but gives back the US Equity and International Equity I lost by selling XGRO7.
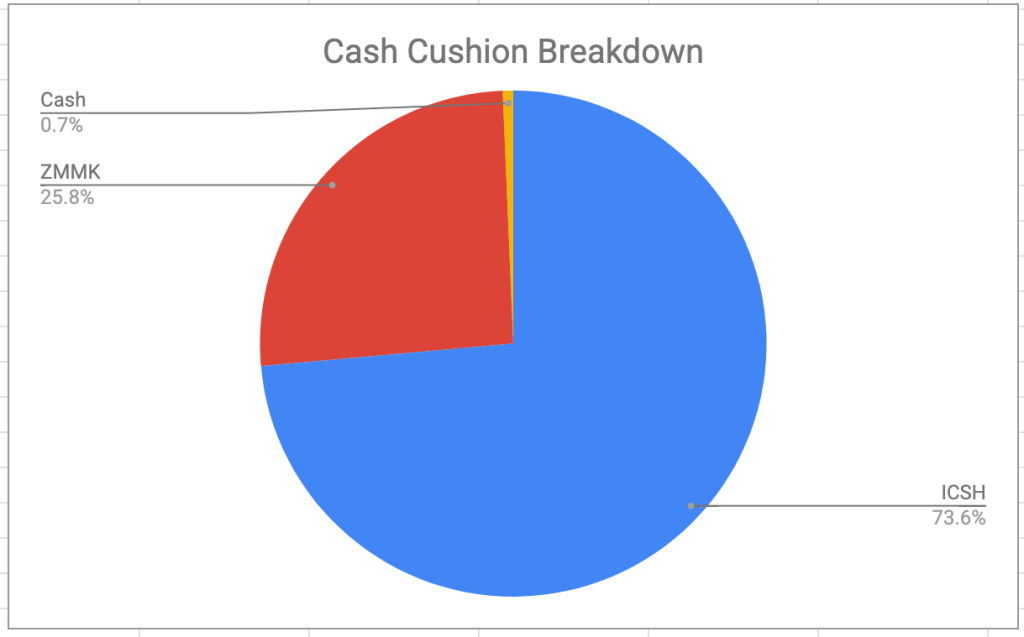
This is how the two accounts break down now, both from an ETF and an asset-allocation perspective. (In the asset allocation charts “Income” is the nomenclature I use for “bonds” and “Cash” means actual money as well as ultra-short-term bond funds like ICSH and ZMMK).
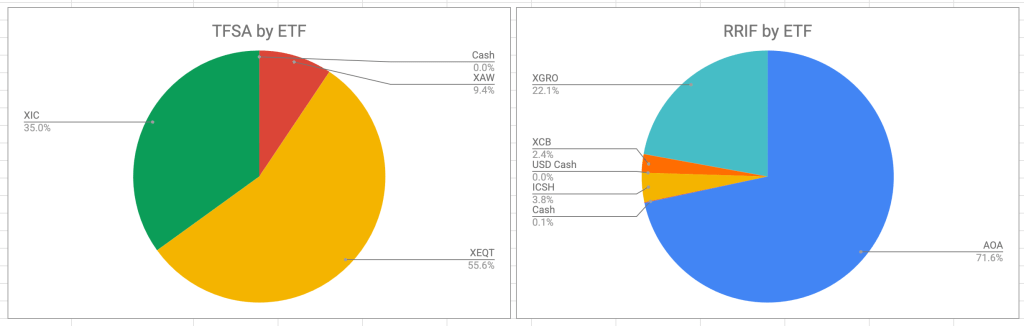
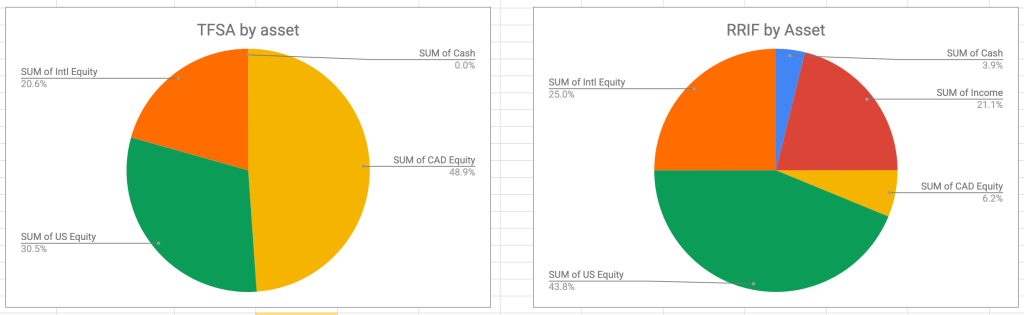
The result is my TFSA is now 100% equity, and the lower-growth cash-generating bonds are now all in my RRIF accounts. More efficient all around!
- Leaving the free money as part of the retirement portfolio was a conscious decision. I could have just as easily decided to withdraw the money every month. ↩︎
- Both ZMMK and ICSH pay monthly. They are both featured in my ETF all-stars. ↩︎
- You can read about it here. ↩︎
- AOA is 50% US equity, 28% International equity. XGRO is 36% US Equity, 24% International Equity. ↩︎
- It’s not a straightforward topic. In the end, the foreign withholding tax isn’t huge but as a cheapskate, it’s noticeable and can be higher than MERs of the ETFs you hold. ↩︎
- XIC helps tilt the overall Canadian equity allocations in the right direction. AOA tilts it in the wrong direction. ↩︎
- The current numbers don’t allow me to use an XEQT/XIC combination. Over time, this will change. ↩︎