The Money Engineer launched in January 2025 and according to the WordPress stats, I made 144 posts last year. What were the most viewed posts of 2025?
5th-ranked post of 2025: ZGRO versus ZGRO.T
I got wind of ZGRO.T through Reddit, specifically r/CanadianInvestor. ZGRO and ZGRO.T are both all-in-one asset allocation ETFs from BMO, but with vastly different yield characteristics. I was confused, but in the end, decided that ZGRO.T was probably not a bad pick for use in a RRIF account as it might save you the hassle of selling shares. Their TOTAL returns (assuming all dividends are invested) are effectively identical.
4th-ranked post of 2025: Spousal RRIF Attribution Rules
I think I was first warned about this nuance of spousal RRSPs/RRIFs by my DIY neighbour (thanks, Steve) and is the main reason I’m only drawing RRIF minimum for the next two years1. I think most of the visits to this article were search-driven. Either that, or people came to admire what might be my favourite article thumbnail2 I’ve posted thus far.
3rd-ranked post of 2025: Norbert’s Gambit with Questrade
As someone who holds more USD-denominated assets than might be wise, I do very much appreciate the existence of a cheapskate way of converting between USD and CAD assets. I think I first learned about this trick via The Loonie Doctor’s blog. The #3 blog entry explains how it works if Questrade is your broker. I would also recommend https://moneyengineer.ca/2025/08/21/tracking-norberts-gambit-costs-with-questrade/ for a very clear picture of what it actually costs (in time and fees) to execute the Gambit: in three of four instances, the time delay of executing the gambit has worked in my favor as the FX rate has drifted a bit to my advantage.
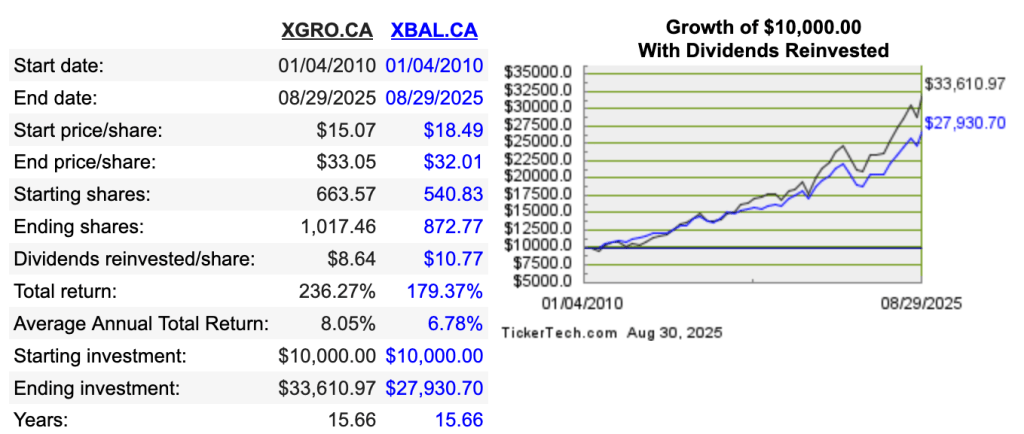
2nd-ranked post of 2025: TD versus iShares all-in-ones
I’m a fan of all-in-ones (and am a little sad https://moneyengineer.ca/2025/01/21/why-you-can-fire-your-advisor-asset-allocation-etfs/ didn’t crack the top five last year). I am genuinely puzzled why people seem to get so wound up about which family of all-in-ones to choose3. I examined TD’s only because their cost to own is a bit cheaper than iShares (who I use primarily), and I’m a cheapskate. (I studied the cost of owning an all-in-one here.) Anyway, in the end, the biggest difference is visible in TGRO versus XGRO because TGRO, unlike any other GRO ETF, uses 10% bond allocation and not 20%. This gooses its return a bit, at the cost of additional volatility. Otherwise, it’s a case of tomato/tomahto. Pick one, or pick them all, it doesn’t matter much.
Top ranked post of 2025: Mini-Review of Optiml.ca
This was, as the title implied, a quick review of a made-in-Canada tool to help craft a retirement plan. And again, my DIY neighbour gave me a heads-up about it4. It got a lot of interest, probably because the kind folks at Optiml linked to my review from their website ;-). I was impressed by the completeness of the tool during my test drive, and it seems like a good and fairly priced way for a DIYer to do some validation of their retirement plan. Having validation of my plan was one of the ways I knew I could retire.
Looking forward to seeing what the 2026 list might look like! Got a topic or question? Send it along to comments@moneyengineer.ca, or comment below!
- RRIF minimum withdrawals are never subject to spousal attribution ↩︎
- Courtesy Pexels free photos, built into WordPress’ editor. ↩︎
- iShares, TD, BMO, Vanguard, Global X…. ↩︎
- Thinking he should write his own blog, maybe. ↩︎